It is becoming increasingly clear that the dominant European model of economic development - based on the great use of resources, creation of waste and pollution - cannot be maintained in the long run. Many of the resources are used only for a short period of time, or they are lost for the economy by disposing or reducing quality during recovery operations.
In recent years the concept of circular economy and related policies have to deal with the use of resources, production, consumption and waste at a higher level. This concept aims to close material losses by maintaining the value of products, materials and resources in the economy as long as possible. This effectively reduces the production of waste and the use of dirty material.
The use of resources, as well as the creation and treatment of waste results in significant environmental pressures during the stages of extraction, production, use and end of the life of the product. Environmental policy goals include reducing the amount of materials used in the economy, improving resource efficiency, reducing waste generation and conversion to a resource. Waste prevention and waste management is a key aspect of the circular economy. Resource efficiency is essential if we want to separate economic development from environmental degradation. The country's resources are limited and their extracting generates environmental impacts and climate. Their more efficient use helps minimize these impacts. In this way, the efficiency of resources is one of the essential elements necessary to create a circular, greener economy in Europe, as well as more sustainable models of production and consumption.
The legislation in the waste management in our country is aimed at promoting a circular economy through the extraction of quality waste resources as much as possible. Furthermore, the policy of the Green Agenda for the Western Balkans relies on several pillars, targeted mainly in the region's reforms to comply with the European Green Agreement (European Green Deal), through the European Union's economic and investment plan. The European Green Agreement aims to promote growth through transition to modern, efficient resources and competitive economy.
The Law on Waste Management provides a legitimate framework for waste treatment and management. It introduces the concept of hierarchy in waste management. The hierarchy is usually adopted is minimizing/reducing source waste, recycling, waste processing (with resource recovery, ie materials (products) and energy), waste transformation (without returning resources) and land depositing Specific approaches are necessary for certain waste categories. Therefore, in addition to the comprehensive Law on Waste Management, there are many other laws in the Republic of Northern Macedonia to deal with different types of waste. The Green Agenda obliges the Western Balkans to move to a circular economy by improving waste management; Increasing resource productivity; Establishing innovative and more efficient ways of producing and consuming and introducing circulating in business models.
Waste regulations aim to protect the environment and human health and help the country's transition to a circular economy. They set goals and strive for:
- Improving waste management,
- Stimulating recycling innovation,
- Limit deposition.
Отпад - Регулатива
- Законот за животна средина
- Закон за управување со отпад
- Базелската Конвенција во врска со контролата врз прекуграничните загадувања со опасен отпад и негово депонирање/Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary movements of Hazardous wastes and Their Disposal. Конвенцијата е ратификувана со Закон за ратификација објавен во (Службен весник на Р.М. 49/97)
- Амандман на Базелската Конвенција во врска со контролата врз прекуграничните загадувања со опасен отпад и негово депонирање и Амандман на АнексⅠ АнексⅧ и АнексⅨ/ Amendment to the basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal. Амандманите се ратификувани со Закон за ратификација (Службен весник на Р.М. бр. 49/04)
- Стратегија за управување со отпад на Република Македонија (2008-2020) година (Службен весник на Р.М. бр. 39/08)
- Национална стратегија за одржлив развој во Република Македонија (2009-2030)
- Закон за управување со пакување и отпад од пакување
- Закон за управување со батерии и акумулатори и отпадни батерии и акумулатори
- Управување со електрична и електронска опрема
- Закон за управување со дополнителни текови на отпад
- Закон за проширена одговорност на производителите за управување со посебните текови на отпад
Отпад - Упатства
Упатство за постапување на општините, општините во градот Скопје и градот Скопје со напуштени или отпадни возила во чекори
УПАТСТВО за водење на постапка за издавање на дозвола за колективен постапувач и за водење на постапка за одобрување или неодобрување на годишен извештај согласно со Законот за управување со пакување и отпад од пакување
Отпад - Обрасци
- Водич за постапка за регистрација
- Документи за дозвола за КОЛЕКТИВЕН ПОСТАПУВАЧ
- Документи за дозвола за САМОСТОЕН ПОСТАПУВАЧ
- Документи за согласност за увоз, извоз и транзит на отпад
- Документи за барање за добивање на дозвола за увоз, извоз и транзит на опасен отпад
- Барање за дозвола за управување со отпад
Отпад - Регистри
Отпад - Дозволи
In the context of the circular economy, waste management focuses on preserving the value and properties of waste materials by delivering high quality secondary raw materials in the economy.
Waste is created in human activities and is seen as an inevitable by-product of economic activities (waste produced by inefficient production processes, from the short-term goods and unsustainable consumption). The creation of waste indicates the loss of matter and energy and imposes the costs of society and the state for the collection, treatment and disposal of waste viewed outside the concept of a circulatory economy.
Waste is one of the main environmental problems in many European countries, and even in the Republic of Northern Macedonia, taking into account the fact that the amount of waste is constantly increasing.
Most of the waste in the Republic of Northern Macedonia is deposited on the legal and illegal-so-called illegal dumps. Waste recycling in the Republic of Macedonia is slightly present. Impact of landfills on the environment, and thus human health is high because greenhouse gases (methane), organic micropolutants (dioxins and furanes) are emitted, volatile heavy metals in the air and leakage of landfills emitted in the soil. and groundwater and which may contain toxic substances.
Important are initiatives to promote the processes of reducing the amount of waste, its recycling and implementing safe standards for waste disposal.
The primary goal in European Union countries as well as in the Republic of Northern Macedonia is to establish a strong link between economic growth, the use of natural resources and waste production, in order to reduce the burden on the environment.
in Second Environmental Action Plan of the Republic of Macedonia has listed certain goals regarding waste and integrated management with waste, efficient institutional and organizational setup and improved waste management infrastructure
According to the waste legislation in the Republic of Northern Macedonia, the priorities for waste management are the following:
- avoiding waste creation and reducing the harmful effects of waste on the environment, life and health of human beings,
- Improving production technologies that reduce waste creation and use of environmental products and less packages,
- Recycling and reuse of waste or in another process of extraction of secondary raw materials, or to be used as an energy source.
Главно создавањето на отпад доаѓа од производствените активности, од каменоломите и рудниците, од градежништвото, отпад од земјоделството и шумарството, комуналниот отпад итн.
Отпадот од производствените активности се состои главно од храна, дрво, хартија, хемикалии, неметални минерали, базични метали и друго. Производствените активности можат да имаат централна улога во редуцирањето на количината на генерираниот отпад со:
- Инкорпорирање на анализите за животниот циклус во дизајнирањето и производството на стоки и сервисни услуги,
- Промоција на одржливо користење на материјата и енергијата,
- Елиминација или редуцирано користење на субстанциите и материјалите кои се опасни за здравјето на луѓето и животната средина.
A list of types of waste has been adopted.
- municipal waste
- mines and quarry waste
- electricity production waste
Комунален отпад
Комуналниот отпад е еден од основните текови отпад што се создава.Комунален отпад е отпадот од домаќинствата, како и друг отпад кој се создава во комерцијалниот и индустрискиот сектор кој поради неговите карактеристики, состав и количина е сличен со отпадот од домаќинствата. Отпад од домаќинствата е отпад кој редовно се собира од домаќинствата, вклучувајќи го и отпадот што се остава на собирните места и собирните центри и одделно собраниот опасен отпад од домаќинствата, кабаст отпад, отпадот од градинарството и така натаму.Околу 78% од населението е вклучено во јавниот систем на собирање на комунален отпад, што го извршуваат јавните претпријатија. Останатото население (22%) кое не користи комунални услуги, во најголем дел е концентрирано во руралните населени места. Општа практика е собирање на несепариран комунален и неопасен индустриски отпад како и несепарирани неопасни и опасни фракции на отпад.
Усвоен е и Правилник за општите правила за постапување со комуналниот и со другите видови неопасен отпад.
Преработка и рециклирање на отпад
Активностите на преработка и рециклирање за комуналниот отпад се многу ограничени. Во однос на рециклирањето, општините не организираат посебно собирање на биоотпад или суви рециклирачки материи во Северна Македонија. Постојат некои маргинални активности за рециклирање, со неформални собирачи на отпад што го собираат отпадот од депонии и канти. Воспоставените системи за отпад од пакување, батерии и акумулатори, електрична и електронска опрема се воспоставени од страна на организациите за Проширена одговорност на производителот, во договор со општините и другите субјекти вклучени во шемата за проширена одговорност на производителот.
Правилникот за количеството на биоразградливи состојки во отпадот што смее да се депонира е преку примена на превенција, рециклирање, компостирање, производство на биогас или други начини на искористување на материјата и енергијата на биоразградливиот отпад да се постигне намалување на количеството биоразградливи состојки во отпадот што се депонира. Голем дел од растителното ткиво што се произведува во земјоделството се искористува повторно, на начин што е поволен за животната средина. Ѓубривото добиено од крупната и од ситната стока се искористува во целост за ѓубрење на почвата.
Во однос на отпадот од пакување е организиран формален систем за негово собирање и рециклирање разработен во соодветниот закон.
Постои законската регулатива за третирање на отпадните гуми каде е наведено дека при постапка на преработка на отпадни гуми, рециклирањето има предност во однос на нивното искористување во енергетски цели. Преработката треба да опфати најмалку 70% од количините на увезени нови гуми од претходната година во Република Македонија.
Законската регулатива за отпад од искористени возила, е насочена кон спречување на создавање на отпад од искористени возила, со тоа што промовира можност за организирано собирање и постапување со искористените возила, со можност за повторна употреба на одредени нивни градбени компоненти и материјали, потоа нивна рециклажа и соодветно отстранување на отпадот. При тоа ќе се има увид на сите увезени возила, потоа на сите искористени возила преземени од страна на собирните пунктови, како и на количините на компонентите и материјалите за понатамошна преработка, рециклирање и отстранување, како и на опасните компоненти од размонтираните искористени возила.
Интегрирана мрежа за отстранување на отпад
Претставува системот на објекти и инсталации за постапување со отпад кои се меѓусебно поврзани (примарен систем за собирање на отпад, претоварни станици, секундарни транспортни системи, депонии). Усвоен е Правилник за минималните технички услови во поглед на заштита на животната средина кои треба да ги исполнуваат претоварните станици, условите што треба да ги исполнуваат локациите на кои што се градат односно се поставуваат претоварните станици, како и роковите за чување на отпадот во претоварните станици според видовите на отпад.
- Правилник за начинот и условите за функционирање на интегрираната мрежа за одстранување на отпадот
- Правилник за минималните технички услови
Во Правилникот за начинот и условите за складирање на отпадот, како и условите што треба да ги исполнуваат локациите на коишто се врши складирање на отпад се пропишани видовите и начините на складирањето, утврдувањето на карактеристиките на отпадот непосредно пред складирањето, како и општите услови на системот за заштита, контрола и одржување на локациите за складирање на отпадот. Во правилникот е дадена и индикативната листа на некомпатибилни отпади и материјали.
Отстранување на комуналниот и друг вид на неопасен отпад
Цврстиот отпад што се создава во Република Македонија, во најголем дел се отстранува на депонии. Илегалните депонии за комунален отпад се доста застапени особено во руралните предели. Депониите претставуваат ризик во поглед на загадувањето на воздухот, почвата, површинските води и подземните води. Поседуваат и потенцијални ризици за биодиверзитетот, земјоделското земјиште и здравјето на луѓето, како последица од депонирање на неселектиран опасен и неопасен отпад.
За регулирање на работата на депониите постојат неколку подзаконски акти како што се правилникот за условите кои треба да ги исполнуваат депониите, во кој се пропишуваат условите кои треба да ги исполнат депониите заради спречување и намалување на штетните влијанија на отпадот врз животната средина, животот и здравјето на луѓето.
Условите за прифаќање на отпадот во одредена депонија, врз основа на видот и составот на отпадот, способноста за формирање на исцедок, промените на состојбата односно однесувањето на отпадот на подолг временски период и попрецизни податоци за општите својства на отпадот што треба да се депонира се наведени во:
При наведување на критериумите за прифаќање на отпадот на соодветна класа на депонија треба да се земе во предвид заштитата на животната средина и заштита на здравјето на луѓето. За определување на општите својства на отпадот се определува количината на органските материи во отпадот, биоразградливоста на органските материи во отпадот, екотоксиколошките својства на отпадот итн., преку определување на основен растворен органски јаглерод, вкупен органски јаглерод, вкупно растворливи честички, тешки метали, сулфити, хлориди, феноли и др.
Целите се превенција и редукција на негативните ефекти на депониите врз животната средина односно површинските и подземните води, почвата, воздухот и здравјето на луѓето. Правилникот предвидува следење на состојбата на телото на депонијата, следење на површинските и подземните води во непосредна близина на депонијата, следење на гасовите од депонијата, следење на емисиите во воздух од депонијата, следење на емисиите во воздух од постројките за горење гас на депонијата и др.
- Правилник за начинот и постапката за работа, следење, работа и контрола на депонијата
- Правилник за формата и содржината на барањето за основање на депонија за неопасен и инертен отпад
- Правилник за дозвола за оператор на депонија
- Правилник за отстранување на отпад, и начинот за обука и тренинг на вработените
Отстранувањето на отпадот по пат на горење или согорување се врши во посебно конструирани инсталации, во зависност од видот на отпадот. Инсталациите за горење или согорување, вклучувајќи ги и сите подготвителни помошни и сервисни објекти, уредите и опремата кои се во функција на уредот и опремата за горење и за согорување, треба да бидат конструирани и да работат така што ќе се спречи да дојде до надминување на граничните вредности на загадувачките супстанции кои се испуштаат во воздухот, почвата и во водите, испуштањето мириси и бучава, како и да се обезбеди заштита на животот и на здравјето на луѓето.
Отпадот од рудниците и каменоломите
Отпадот од рудниците и каменоломите може да препокрие голема површина на земјиште и да има штетно влијание врз воздухот, водата и почвата освен ако не е добро управуван. Различни активности во рударството и каменоломите резултираат со значајни количини на неупотребени материјали, од различна природа и со различна потенцијална опасност.
Отпадот од продукцијата на електрична енергија
Количината на отпадот од трансформација на енергијата зависи од употребеното гориво, но некои податоци за количината на создадениот отпад може да произлезат од количината на продуцираната електрична енергија. Хидроелектраните и електраните кои работат на гас не генерираат цврст отпад. Додека термоелектраните кои работат на јаглен и други фосилни горива продуцираат голема количина на отпад како пепел и друго. Тоа значи дека поместување на производството на електрична енергија кон почисти и обновливи извори за производство на енергија ќе резултира со редукција на количеството на отпадот.
Отпад генериран со активности во градежништвото
Отпад генериран со активностите на конструкција и уривање на објекти во градежништвото, може да содржи опасни супстанции како што е азбестот, кој може да е присутен во големи количини кога старите згради се рушат и реновираат. Голем број на компоненти во отпадот кој се создава во градежништвото можат да се рециклираат и да заменат до 10 % од основните супстанции.
Опасен отпад
Опасен отпад е отпадот што содржи супстанции кои имаат едно или повеќе својства како што се: експлозивност, реактивност, запаливост, надразливост, токсичност, инфективност, канцерогеност итн. Како резултат на опасните супстанции кои ги содржи опасниот отпад тој претставува сериозен ризик за животната средина и здравјето на луѓето ако не се управува со него правилно и безбедно. Одредени сектори во економијата продуцираат опасен отпад, а како најголем меѓу нив е производствената индустрија. Како што е случајот и со останатиот отпад, така и со опасниот отпад, воспоставувањето на законска регулатива, соодветна обука на персонал за управување со истиот, како и зголемување на јавната свест се главните елементи за безбедно управување со опасниот отпад.
Опасниот отпад поседува поголем ризик за животната средина и здравјето на луѓето отколку неопасниот отпад и затоа е потребен строго контролиран режим при управување со истиот кои се регулирани со
Главните принципи на кои се базира управувањето со опасниот отпад се намалување на опасниот отпад и безбедносен транспорт на истиот, намалување на степенот на опасноста на опасниот отпад и соодветно постапување со истиот. Во овој правилник се напишани одредени безбедносни мерки во однос на собирање, постапување и мониторинг на опасниот отпад како и дополнителни мерки во однос на обележување, пакување и означување на опасниот отпад од продуцентот до крајното отстранување или рециклирање. Методите за преработка на опасниот отпад вклучително и повторна употреба, рециклирање и употреба на отпадот како извор на енергија во однос на употребливите супстанции и другите состојки во опасниот отпад треба да се соодветни на видовите и количините на опасниот отпад кој се преработува. Дозволите кои се даваат на инсталациите кои работат со опасен отпад треба да исполнуваат одредени построги критериуми отколку инсталациите кои работат со неопасен отпад.
Полихлорираните бифенили (ПХБ)-Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCB) спаѓаат во групата на синтетички хемикалии кои се познати како перзистентни органски загадувачи-Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs). ПХБ се продуцирани масовно од 30те до 80те години од минатиот век. Тие имаат голема хемиска стабилност и резистентност на топлина и широко се употребуваат како компоненти на електричната и хидрауличната опрема како и подмачкувачи. Се употребуваат во затворени апаратури како диелектрични течности во електричната опрема како што се трансформаторите, кондензаторите, хидрауличните системи. Ги има во индустриски масла, бои, лепила, пластика итн. ПХБ се класифицираат како можни хумани канцерогени и продуценти на разни негативни ефекти кај луѓето и животните вклучувајќи репродуктивна токсичност, имунотоксичност и тератогеност. Во одредени медиуми на животната средина како подземните и површинските води, почвата, па и храната ПХБ може да се транспортираат на големи растојанија и да се детектираат на места далеку од местото на нивно производство или употреба. Идентификацијата на локациите со трансформатори што содржат ПХБ е во тек и веќе се врши отстранување (горење во странство)
Маслата за подмачкување се вообичаено користен продукт во нашиот секојдневен живот кои им овозможуваат на моторите и машините да ја извршуваат својата функција. Во текот на нивното користење маслата ги губат нивните особини и се контаминираат. Така искористените масла по одредено време се заменуваат со нови масла за подмачкување.
Отпадните масла спаѓаат во групата на опасен отпад поради своите опасни карактеристики. Отпадните масла кои се наоѓаат во реките и езерата го загрозуваат водниот жив свет. Само едно литро отпадно масло може да контаминира милиони литри на вода. Контаминација на почвата се јавува како резултат на истурени отпадни масла на површината на земјата. Се креира систем за собирање, чување, регенерирање и отстранување на отпадните масла, а се со цел да се спречат негативните ефекти врз животната средина и да се извлече економски бенефит со регенерација на отпадните масла.
Пропишани се и начини на постапување и обележување на медицинскиот отпад, како би се намалило негативното и штетно дејство врз животната средина и здравјето на луѓето. Сепаратното собирање на медицински отпад во болниците и во другите здравствени институции се развива бавно.
Правните и физичките лица кои создаваат, поседуваат или преработуваат титаниумдиоксид се должни до надлежниот орган за вршење на стручни работи од областа на животната средина-Управата за животна средина, да достават податоци за отпадот од титаниумдиоксид, кој е наменет за отстранување, како и да вршат мониторинг на почвата, водите и на воздухот на местата каде се преработува, складира и се отстранува отпадот од титаниумдиоксид, како и на околната зона којашто се смета за незагадена.
Трендови во управување со отпадот
Сегашната законска регулатива во однос на отпадот се базира на концептот на хиерархија во управувањето со отпад. Ова значи во идеален случај отпадот треба да се превенира, а додека она што не може да се превенира треба повторно да се искористи, обнови или рециклира колку што е можно повеќе. Додека пак депонирањето на отпадот на депонии треба да се користи што е можно помалку, бидејќи е најлошата опција за животната средина и укажува на губење на ресурсите. Хиерархијата во управувањето со отпадот не треба да се гледа како тешко достапна и брзо достапна цел, особено кога се има во предвид дека постојат различни методи на третман на отпадот кои имаат и различно влијание врз животната средина. Целта на придвижување кон рециклирање и обновување на отпадот претставува придвижување кон хиерархијата во управување на отпадот и намалување на користењето на депониите.
Превенцијата на генерирање на отпадот би требало да заземе иницијално место, бидејќи редуцирање на отпадот подразбира и редуцирање на потребата за негово собирање и третман кое е во корелација со трошоците и влијанието врз животната средина. Превенција на создавањето на отпад во смисла на употреба на материјали, добра, сервиси на таков начин што нивното производство, употребата, реупотребата, рециклирањето ќе резултираат со најмало можно производство на отпад. Превенцијата е само еден дел од концептот на почисто производство.
Можеби најголем предизвик претставува воспоставувањето на соодветенциклус за рециклирање на отпадот.
Инсенерација или согорување на отпадот со искористување на енергијата е уште една опција за избегнување на депониите.
Депонирање на отпадот на депонии е најдолната можна опција во хиерархијата на управување со отпадот, но сеуште најдоминантен метод користен кај нас. Депониите во нашата земја најчесто се неправилно управувани и не ги задоволуваат минималните стандарди во однос на животната средина и здравјето на луѓето. Голем предизвик е да се достигнат одредени стандарди при градењето на депониите и да се затворат несоодветно управувани и одржувани места.
Точни и навремени податоци за отпадот се едни од главните елементи за долгорочна превенција на илегалните места на депонирање на отпадот. Несоодветни податоци може да доведат до несоодветни одлуки во однос на законската регулатива за отпадот како и воспоставување на несоодветна инфраструктура за управување со отпадот.
Управувањето со отпадот во нашата земја сеуште претставува проблем, бидејќи количината на отпадот е во постојан пораст, а законската регулатива во одредени случаи слабо се имплементира.
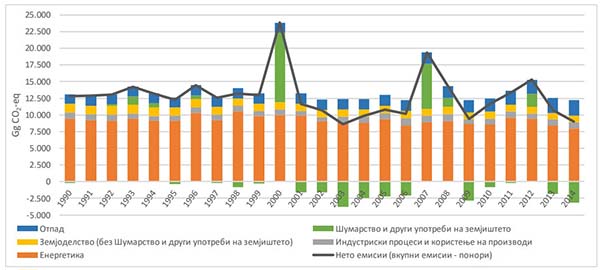
Емисиите на стакленички гасови од секторот „отпад“
Емисиите на стакленички гасови од секторот отпад ги опфаќаат следните категориите: депонии за цврст отпад, биолошки третман на цврст отпад, согорување и отворено горење на отпад и третман и испуштање на отпадни води. Вкупните емисии од овој сектор се проценети на 2.226,1 Gg CO2-eq во 2013 и 2.323,5 Gg CO2-eq во 2014. Најзначајни се емисиите од депониите на цврст отпад кои покриваат 94,4 % од вкупните емисии од овој сектор во 2014 година. Емисиите од согорување и отворено горење на отпад претставуваат 1,4% од вкупните емисии од отпад. Преостанатите 4.2% од емисиите на стакленички гасови од овој сектор потекнуваат од третманот и испуштањето на отпадните води (од домаќинствата и од индустријата). Емисиите на CH4 сочинуваат 97,6% од вкупните емисии (изразени во CO2-eq) од секторот отпад во 2014 година. Емисиите на CO2 од овој сектор во СевернаМакедонија се јавуваат само како резултат на отвореното горење на отпадот и учествуваат со 0,4% во вкупните емисии од секторот, додека емисиите на N2O претставуваат 2% од вкупните секторски емисии. Најголем удел имаат емисиите од секторот енергетика, со 65,2% во 2014, а после тоа се секторот отпад со 19%.
Увоз, извоз и транзит на отпад
Увоз, извоз и транзит на отпад во Република Северна Македонија се врши согласно членовите 92,93,94,95,96,97 од Законот за управување со отпад. Увоз, извоз и транзит на отпад во Република Северна Македонија се врши според Базелската конвенција за контрола на прекуграничното пренесување на опасен отпад и негово складирање.
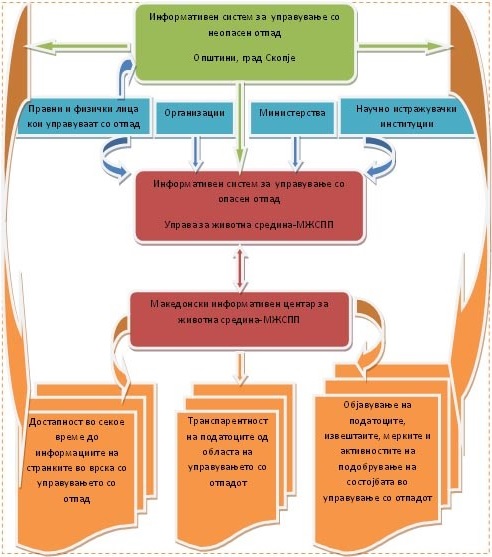
Информативен систем за управување со отпад
Министерството за животна средина и просторно планирање организира информативен систем за управување со отпад, како дел од севкупниот Македонски информативен систем за животна средина. Организационите единици за регионално управување со отпадго организираат информативниот систем на локално ниво, со кој се обезбедува собирање и презентирање на податоци за состојбата во врска со управување со неопасниот отпад. Организационите единици за регионално управување со отпадсе должни добиените податоци за состојбата во врска со управување со неопасен отпад да ги достават до надлежниот орган за вршење на стручни работи во животната средина-Управата за животна средина.
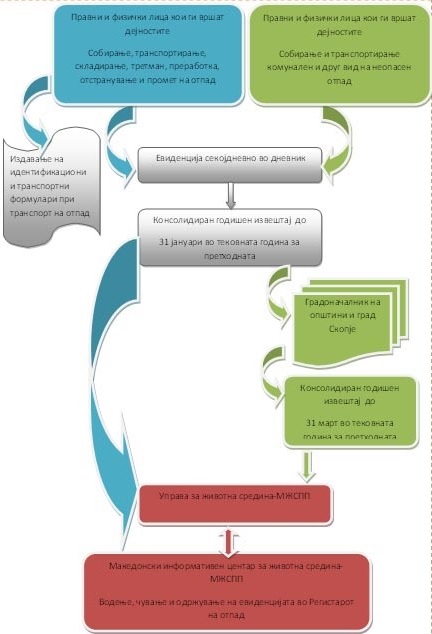
Евиденција на отпад
Формата и содржината за евиденција, како и содржината на годишните извештаи е пропишана во:
- Правилникот за формата и содржината на дневникот за евиденција за постапување со отпад
- Правилник за содржината и начинот на водење, на евиденцијата во регистарот на отпад
Дневник за евиденција
Надлежни органи на Законот за управување со отпад
Надзор над примената на Законот за управување со отпад и прописите донесени врз основа на овој закон, врши органот на државната управа надлежен за работите од областа на животната средина-Министерството за животна средина и просторно планирање. Инспекцискиот надзор над примената на Законот за управување со отпад и на прописите донесени врз основа на овој закон го врши Државниот инспекторат за животна средина.
За работите од надлежност на општините, општините во градот Скопје и градот Скопје утврдени со овој закон инспекцискиот надзор над примената и спроведување на овој закон го вршат овластени инспектори за животна средина на општините, општините во градот Скопје и овластени инспектори за животна средина на градот Скопје.
Инспекциски надзор над примена на истиот закон во делот на прометот со производи и пакувања, означувањето на производите и пакувањата и информирањето на потрошувачите го врши државниот пазарен инспектор. Додека инспекцискиот надзор над примена на законот во делот на создавање, селектирање и пакување на медицинскиот отпад врши државниот санитарен и здравствен инспекторат, во соработка со државниот инспектор за животна средина.
Инспекциски надзор над примената на овој закон во делот на управување со неопасен отпад врши Државниот комунален инспекторат. Надзор над спроведување на прописите донесени од Регулаторната Комисија врши Регулаторната Комисија. Надзор над спроведувањето на обврските од страна на субјектите кои транспортираат отпад во однос на обврската за поседување на транспортни и идентификациони формулари како и обрасците од членот 96 Дозволи и согласности за извоз, увоз и транзит на отпад, ставови (7) и (8) од овој закон, врши Царинскиот орган и органот на државна управа надлежен за вршење на работите од областа на внатрешни работи.
Одредбите од Законот за управување со отпад се однесуваат на сите видови отпад наведени во Листата на видовите отпад освен на наведените отпади во членот 2 (Примена на законот), од Законот за управување со отпад.
Situation in the Republic of Macedonia regarding waste data and implementation of waste data collection systems
Margareta Cvetkovska, Violeta Panovska,
- Ministry of Environment and Physical Plannin
M.Cvetkovska@moepp.gov.mk - State Statistical Office
Dame Gruev 4, 1000 Skopje, Republic of Macedonia
Tel.: +389 02 3295 719; Fax +389 3111 336
Violeta.panovska@stat.gov.mk
Situation in the Republic of Macedonia regarding waste data and implementation of waste data collection systems
Waste management is one of the most serious environmental issues in Macedonia. It is characterized as sub-standard with regard to human and financial resources, insufficient and ineffective with regard to monitoring and law implementation as well as hampered by political and social lacks (like execution of enforcement, stakeholders consultations, public awareness), and also characterized with lack of data and information on the local and national levels.
Waste management policy
The general waste management policy with intention to overcome the current situation and to establish a sustainable waste management system was formed in: The Law on Environment (which includes basic stipulations on environmental permitting, EIA procedure and greenhouse gas emissions), The National Environmental Programmes (NEAP 1996/2006), and The Law on Waste Management (2004).
Transposition of EU legislation on waste management into the national waste management legislation framework is one of the main and priority tasks in the establishing process of the proper waste management system in Macedonia. The detailed procedures about different waste stream issues are provide through secondary legislation.
Tasks and responsibilities of MoEPP and municipalities
Tasks and responsibilities of MoEPP on waste management is planning and policy development, registration, issuing permits and licensing, organization an effective solid waste management system for hazardous waste, monitoring, data collection/handling, inspection. Currently MoEPP have insufficient knowledge and experience to develop and implement all relevant standards and instruments as required by the new waste legislation.
The municipalities are responsible for activities: Organization the collection, transportation and disposal of municipal wastes; Supervising transportation and disposal of industrial non-hazardous waste; Deciding on the location of waste management facilities, issuing local regulations on waste management facilities; Establishment of the non hazardous and inert waste landfills; Issuing environmental permits (IPPC B-permits). Only few municipalities have established or designated divisions or persons in their administration/structure to deal with waste management.
According to legislation the municipalities and MoEPP have to receive yearly reports from legal and natural persons holder of waste about accepted waste and produced waste (origin, type, quantity, treatment), transferred waste ( type, quantity, to whom). Also MoEPP has to receive yearly reports from mayor of municipalities about transported municipal and non-hazardous waste, disposed municipal, non-hazardous, and disposed inert waste. The municipalities and MoEPP have to receive yearly reports from landfills about accepted municipal, non-hazardous, and inert waste, general data for the landfills and accepted steps in the activity of landfills. The implementation and maintenance of a data collection/information system shall cover data on the sources, nature, quantities and fate of waste, the main information on facilities for recovery, recycling and energy utilization of constituents of individual waste streams and Information on final disposal facilities.
Management of waste
Almost the only method for the final disposal of waste in R. of Macedonia is deposition on landfills.
Only some hazardous waste from health institutions and some liquid hazardous waste are incinerated and co-incinerated. Macedonia has limited markets for materials and products recovered from waste with intention of recycling or utilization for energy production. The majority of recovered material for recycling would have to be exported, which will incur additional costs for handling and shipping and thus may exceed the market value of the materials.
State Statistical Office (SSO)
According the Low on State Statistics, the State Statistical Office is unique official statistics provider in the country.
Five year statistical Programmes (adopted by Government) and the annual programmes are the basic acts where the whole statistics activities are provided.
By 2006, an Agreement for cooperation between State Statistical Office and Ministry of Environment and Physical Planning was signed. It covers close cooperation in terms of different projects, including the area of environmental statistics.
Following the needs, project activities and the current situation, ES activities in following areas are provided in the five year Statistical Program 2008 – 2012: waste statistics, water statistics and environmental expenditures.
The main objectives refer on waste statistics at SSO are:
- to meet WStatR and national requirements on: generated, treated, received and delivered waste
- international reporting (OECD Joint Questionnaire)
Having in mind that National legislation of the issue is responsibility of Ministry of Environment and Physical Planning, its necessary to mention that the process of adjustment with EU legislation is ongoing; some acts are adopted and already in use some are waiting of adoption; some are in preparation phase and some are planned to be prepared – so the actual situation of adjustment process is directly reflected on ES activities at SSO. In general there is very solid legal base, but the time period provided for appliance is still going on.
SSO and MoEPP were involved in three-year regional SIDA project for developing ES in the Balkan from 2005-2007, waste statistics was one of prioritized area in the project. Since 2008, SSO is involved in National SIDA three year environmental project, where waste statistics is provided as a first priority in the project activities
What’s done until now in the field of waste statistics at SSO?
Introduction with:
- EC Waste Statistic Regulation No 2150/2002 and Waste Statistical Methodology
- planning data collection processes (methods and organization)
- Connections between National List of waste and EW Categories are made according to the National legislation and EU regulation
In order to provide Pilot survey on waste from industries methodological instruments are prepared (questionnaire, manual, classification, codes, logical control) in accordance with National legislation and EWStat Reg.
Pilot survey with main goal to test the questionnaire an the response rate was conducted from 15 – 26 September 2008 (the Pilot results cross over our expectations with the content of the questionnaire and response rate from over than 80%)
Future planes – to provide the whole survey on waste from industries (2009) and to provide revised survey on municipal waste and published national data on municipal waste for the first time (2009/2010)
Expectations – reporting to EUROSTAT data from waste from industries after conducting the survey and data processing.


